Usage
Basic example
Import AISim plus numpy and matplotlib and print current version:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import aisim as ais
print(ais.__version__)
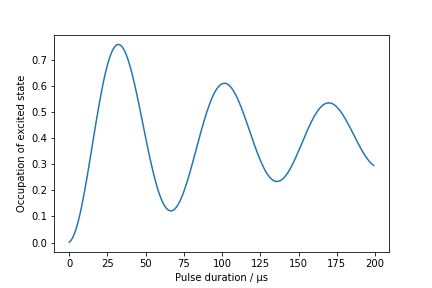
As an example, we simulate Rabi oscillations driven by stimulated Raman transitions in the presence of thermal motion.
Note
If not explicitly stated otherwise in the docstring, units are assumed to be SI units without prefixes, i.e. meters or Kelvin. The only exception is kilogram.
First, we define a AtomicEnsemble object for atoms from a
magneto-optical trap after sub-Doppler cooling:
# spherical atomic cloud with radius 3 mm
pos_params = {
'mean_x': 0.0,
'std_x' : 3.0e-3,
'mean_y': 0.0,
'std_y' : 3.0e-3,
'mean_z': 0.0,
'std_z' : 3.0e-3
}
# cloud velocity spread in m/s at tempearture of 3 μK in x and y,
# and 150 nK in z (after a velocity selection process):
vel_params = {
'mean_vx': 0.0,
'std_vx' : ais.convert.vel_from_temp(3.0e-6),
'mean_vy': 0.0,
'std_vy' : ais.convert.vel_from_temp(3.0e-6),
'mean_vz': 0.0,
'std_vz' : ais.convert.vel_from_temp(150e-9)
}
# generate an AtomicEnsemble of 10000 atomsin the ground state
atoms = ais.create_random_ensemble_from_gaussian_distribution(
pos_params,
vel_params, int(1e4),
state_kets=[1, 0])
Only a fraction of these atoms will be detected after a time-of-flight of 800 ms. We model the detection region with radius of 5 mm:
det = ais.Detector(r_det=5e-3, t_det=800e-3)
We setup the two counter-propagating Raman laser beams with a wavelength
of 780 nm, 30 mm beam diameter and a Rabi frequency of 15 kHz as
IntensityProfile and WaveVectors objects:
intensity_profile = ais.IntensityProfile(
r_beam=15e-3,
center_rabi_freq=2*np.pi*15e3)
wave_vectors = ais.Wavevectors( k1=2*np.pi/780e-9, k2=-2*np.pi/780e-9)
We select the atoms that are eventually detected, let those freely propagate for 100 ms before we start the Rabi oscillations up to 200 μs:
atoms = det.detected_atoms(atoms)
atoms = ais.prop.free_evolution(atoms, dt=100e-3)
state_occupation = []
taus = np.arange(200)*1e-6
for tau in taus:
prop_atoms = ais.prop.transition(atoms, intensity_profile, tau, wave_vectors=wave_vectors)
mean_occupation = np.mean(prop_atoms.state_occupation(state=1))
state_occupation.append(mean_occupation)
Finally, we plot the results:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(1e6*taus, state_occupation)
ax.set_xlabel('Pulse duration / μs')
ax.set_ylabel('Occupation of excited state');
More examples
The notebooks containing the following exampels can also be found here: